Russia named as likely source of Europe radioactivity spike
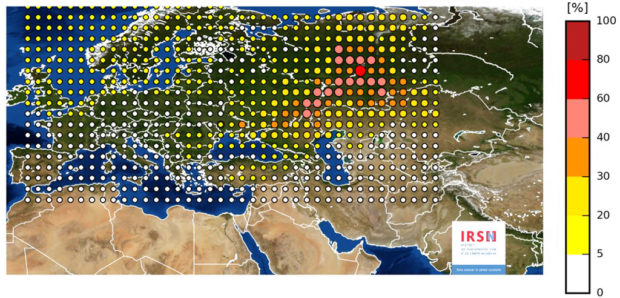
This photo provided on Friday Nov. 10, 2017 by the INRS, Institute for Radiological Protection and Nuclear Safety, shows a map of the detection of Ruthenium 106 in France and Europe. An apparent accident at a Russian facility is suspected of causing a recent spike in radioactivity in the air over much of Europe, according to a report by France’s nuclear safety agency. (INRS via AP)
PARIS (AP) — An apparent accident at a Russian facility is suspected of causing a recent spike in radioactivity in the air over much of Europe, according to a report by France’s nuclear safety agency.
The Institute for Radiological Protection and Nuclear Safety says the release of the isotope Ruthenium-106 posed no health or environmental risks to European countries. It said the “plausible zone of release” was between the Volga River and the Ural Mountains, and suggested random checks on food imports from the region as a precaution.
In a report released Thursday based on monitoring in multiple European countries, IRSN said the Ruthenium appeared to come from an accident in late September involving nuclear fuel or the production of radioactive material. The French agency said the Ruthenium didn’t appear to come from an accident in a nuclear reactor because that would have released other elements.
Germany’s Federal Office for Radiation Protection said last week that elevated levels of Ruthenium were reported in Germany, Italy, Austria, Switzerland and France since Sept. 29, but posed no threat to public health.
After reports of a Ruthenium-106 leak from a plant in the southern Urals first appeared, Russia’s state-controlled Rosatom corporation said in a statement last month that it hadn’t come from its facilities.
Article continues after this advertisement“The claim that the contamination had a Russian origin is unfounded,” it said.
Article continues after this advertisementThe French report says the radioactivity peaked in late September and early October and affected a “majority of European countries” but is no longer detected in the atmosphere over Europe. However it said if such an accident had happened in France, authorities would set up a perimeter around the accident site to monitor health, safety and food quality.
Ruthenium-106 is used for radiation therapy to treat eye tumors, and sometimes as a source of energy to power satellites.
The French agency also said Ruthenium releases could come from the re-entry of a satellite into the Earth’s atmosphere, but that the International Atomic Energy Agency reported that no satellites powered by Ruthenium re-entered the atmosphere during the time period.
France, which has an extensive nuclear energy industry, has reported a series of low-level nuclear incidents recently but none involving Ruthenium or threats to public health. KI