North Korea sub-launched missile breaches Japan air defense zone
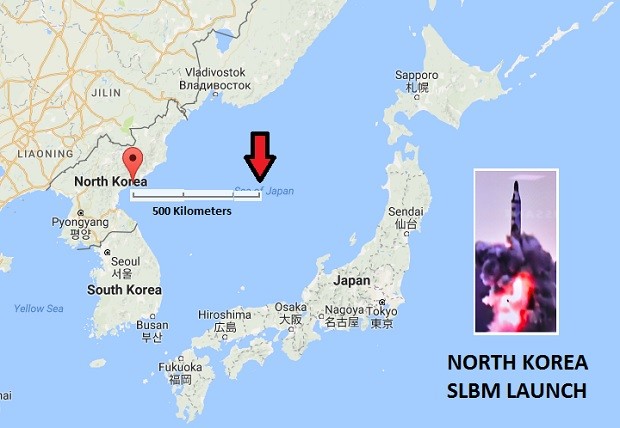
Japan said on Wednesday that North Korea launched a submarine based missile that breached its air defense identification zone and posed a serious threat to its security. The submarine-launched ballistic missile or SLBM was reportedly fired off Sinpo, North Korea, and landed in the Sea of Japan.
SEOUL, South Korea — North Korea on Wednesday fired a submarine-launched missile that penetrated Tokyo’s air defense identification zone (ADIZ) after flying 500 kilometers (around 300 miles) towards Japan.
The flight distance, which was tracked by South Korea’s military Joint Chiefs of Staff, far exceeded any previous SLBM tests, suggesting significant progress in technical prowess.
Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe condemned the missile launch that breached his country’s ADIZ. He called it an “unforgivable, reckless act” and a grave threat to Japan’s security.
READ: North Korea test fires sub-launched missile — Seoul
A proven SLBM capability would take North Korea’s nuclear strike threat to a new level, allowing deployment far beyond the Korean peninsula and the potential to retaliate in the event of a nuclear attack.
“While there are still a lot of questions about the details, this test certainly seems to have been successful,” said Jeffrey Lewis, director of the East Asia Nonproliferation Program at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies in California.
“This system is still in development, but North Korea is clearly making progress,” Lewis told AFP.
Current UN resolutions prohibit North Korea from any use of ballistic missile technology, but Pyongyang has continued to carry out numerous launches following its fourth nuclear test in January.
South Korea has responded by agreeing to deploy a sophisticated US anti-missile system — known as THAAD — a move that has seriously strained relations with North Korea’s main diplomatic ally, China.
‘Effective countermeasure’
Lewis noted that an SLBM was an “effective countermeasure” to THAAD, and other missile defenses with forward-looking radars, since the submarine can launch the missile from behind the radar.
Earlier this month, North Korea fired a land-launched ballistic missile directly into Japanese-controlled waters for the first time, drawing an outraged response from Tokyo.
The latest test came just days after North Korea threatened a pre-emptive nuclear strike against South Korean and US forces who kicked off their annual “Ulchi Freedom” military drill on Monday.
Seoul and Washington insist such joint exercises are purely defensive in nature, but Pyongyang views them as willfully provocative.
The South’s Joint Chiefs of Staff statement said that the North was clearly bent on escalating tensions and said the SLBM test posed a “serious challenge” to security on the Korean peninsula, and represented a grave breach of UN resolutions.
“We will deal strongly and sternly with any provocation by the North,” it said.
Washington also condemned the test and warned Pyongyang against any further provocations.
“Our commitment to the defense of our allies, including the Republic of Korea and Japan, in the face of these threats, is ironclad,” said Pentagon spokesman Gary Ross.
Invasion scenario
The Ulchi Freedom drill plays out a scenario of full-scale invasion by the nuclear-armed North. It is largely computer-simulated but still involves around 50,000 Korean and 25,000 US soldiers.
The exercise always triggers a rise in tensions on the divided peninsula, and this year it coincides with particularly volatile cross-border relations following a series of high-profile defections.
Last week North Korea’s deputy ambassador to Britain, Thae Yong-Ho, defected to the South — a rare and damaging loss of diplomatic face for Pyongyang and a major PR victory for Seoul.
In comments clearly aimed at riling Pyongyang, South Korean President Park Geun-Hye said such high-ranking defections suggested “serious cracks” in supreme leader Kim Jong-Un’s regime.
Park also warned that North Korea may carry out “various terror attacks and provocations” in a show of strength aimed at building national unity and loyalty to Kim.
North Korea has conducted a number of SLBM tests — most recently in April and July — with varying degrees of success.
Previous flight distances have not exceeded 30 kilometers, and the Joint Chiefs of Staff statement acknowledged that Wednesday’s test showed a marked improvement.
The South Korean Defence Ministry has said the North could be able to deploy a working SLBM within three to four years.














